I have recently installed vSphere 6.5 and vSAN 6.6 in our lab, I have got 4 vSAN Hybrid ready nodes , which I will use to setup a vSAN cluster.
Most interesting thing with the 6.5 vSphere release apart from the HTML client and other enhancements is the ability to bootstrap VCSA on a target host by creating a vSAN datastore. With earlier version we used to deploy the VCSA on a temporary data store and later storage vMotioed to the vSAN datastore.
“Jase McCarty” has written a cool blog on the same, you can refer to the below link for details:
Bootstrap the VCSA onto vSAN 6.6
However, I will try to cover the deployment in more details including all the screenshot which can help people deploying vSAN 6.6 for the first time. So let’s get started.
I have installed ESXi 6. 5 on all 4 nodes. It’s time to install the vCenter to configure the vSAN Cluster.
Mount the VCSA installer and run the installer.exe file:
Wizard is similar to previous VCSA 6.x install until we reach the “Install – Stage 1: Deploy PSC” page:

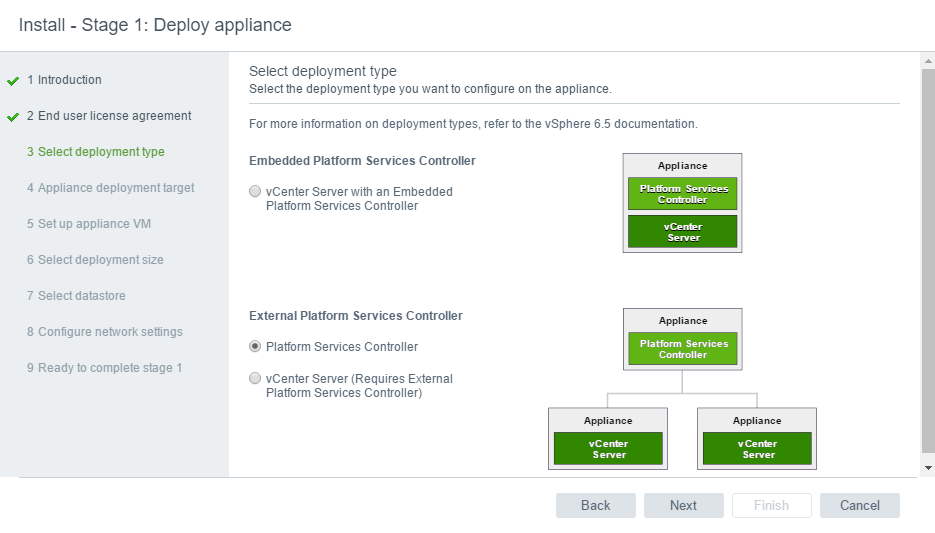
I am deploying the External PSC appliance, however the process is similar for Embedded PSC as well.
The Screenshot is self-explanatory, I am deploying the vCenter appliance on ESXi host “172.24.1.101” .

Select yes for the certificate warning.


This is where we will be creating a vSAN datastore locally on the host and install VCSA. Note that during bootstrapping, you don’t need to have vSAN Network configured on all the nodes. At this moment vSAN Datastore is local to the host, I will cover in another blog post how to expand the vSAN Datastore by claiming the disk from other nodes in the cluster.

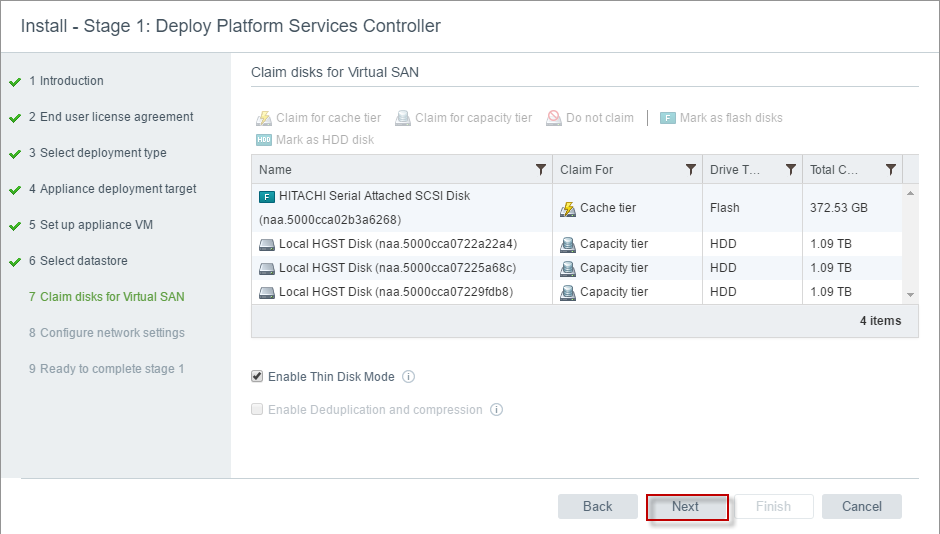
Provided you are using a vSAN compatible controller and Drives, ESXi will detect the flash and HDD resources in the server. In case ESXi is not detecting Flash or HDD, you can manually tag local storage resources as SSD or HDD in this step. For checking the vSAN compatibility, refer to the link below:

Enter the required networking details for the PSC, make sure to configure the DNS host name resolution (forward and reverse) of PSC before deployment .

Finish and wait, the deployment took less than 5 minutes

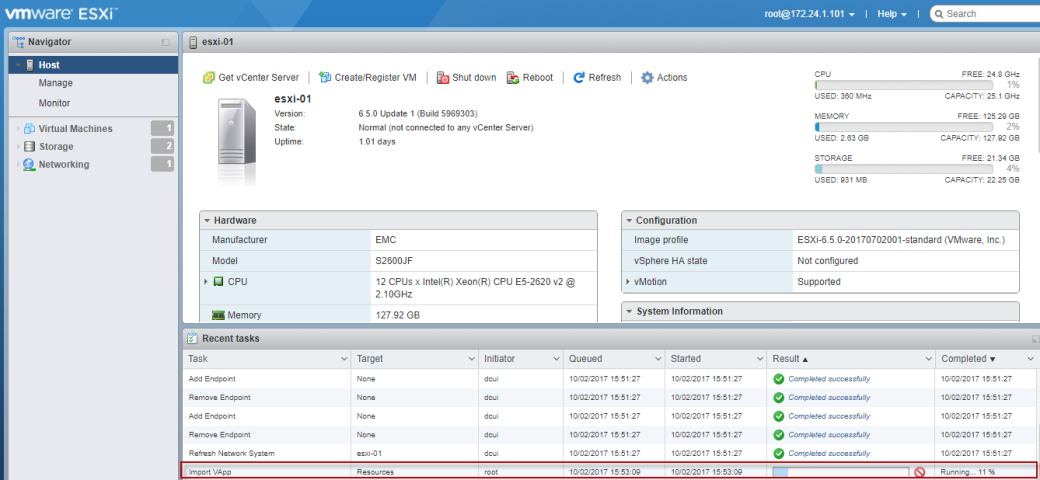

Looking at the host client, I can now see a new “vSAN datastore” and PSC getting deployed on newly created vSAN Datastore.

Once done, we need to configure the appliance size and SSO in stage 2, refer to the below screenshots:



Here you can either join the PSC to an existing SSO (if exists) to run a linked mode configuration or if it is a new deployment select the “create new SSO domain”.
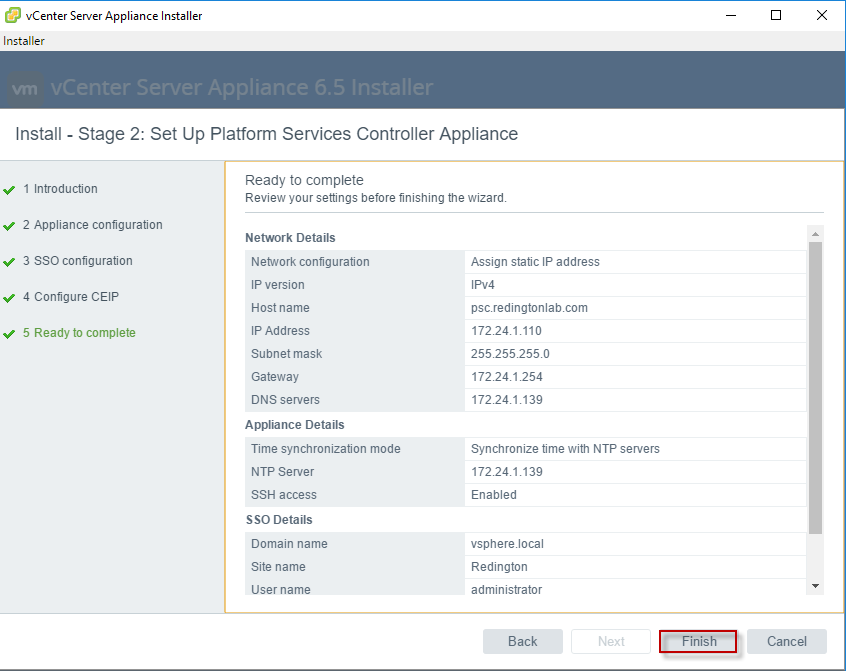

That’s it for PSC deployment, now we need to run the same installer, this time we will install the vCenter server.





Select the vSAN datastore created during the PSC installation.
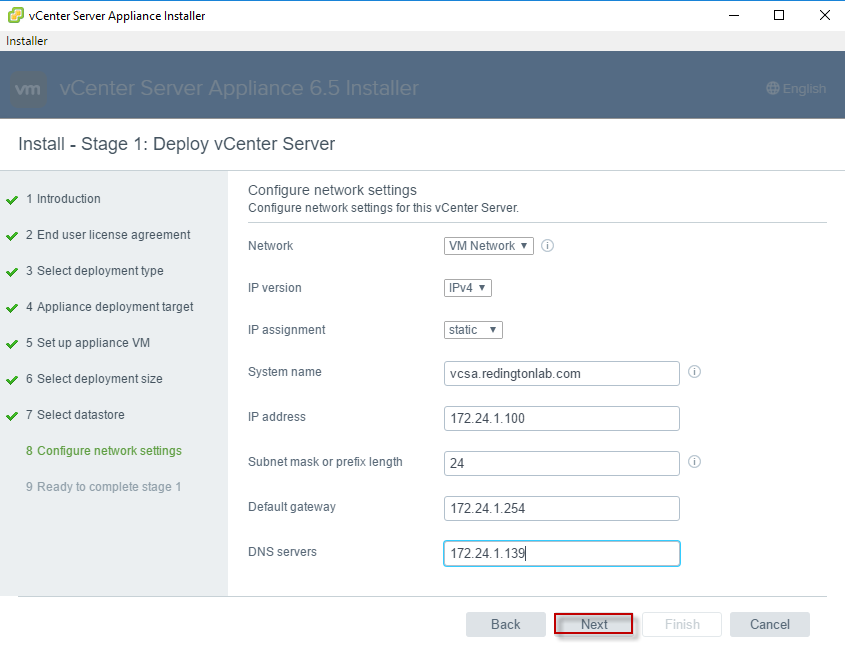
Enter the network configuration for the vCenter server:



Finish and wait, you can actually see the VCSA deployment progress by login in to the target host.

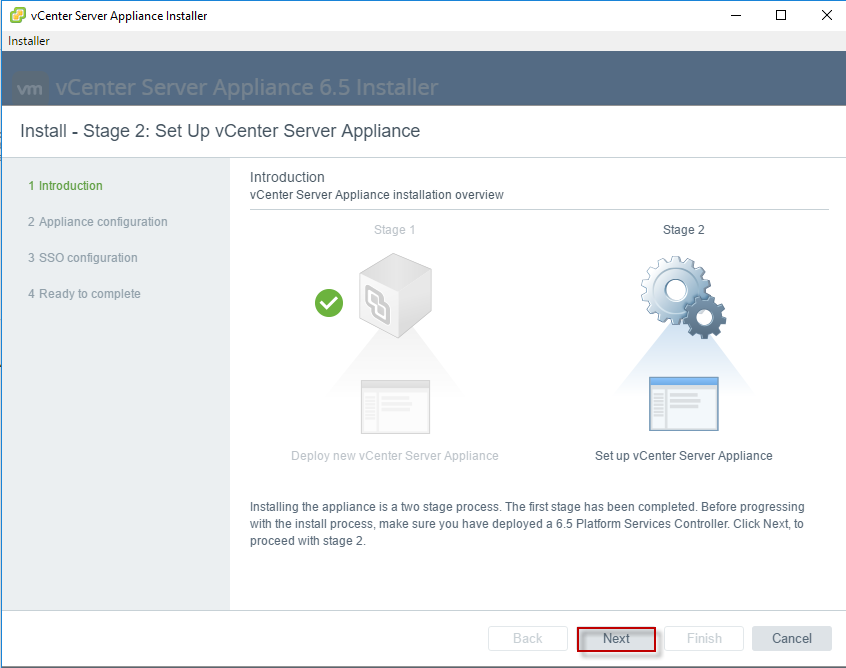
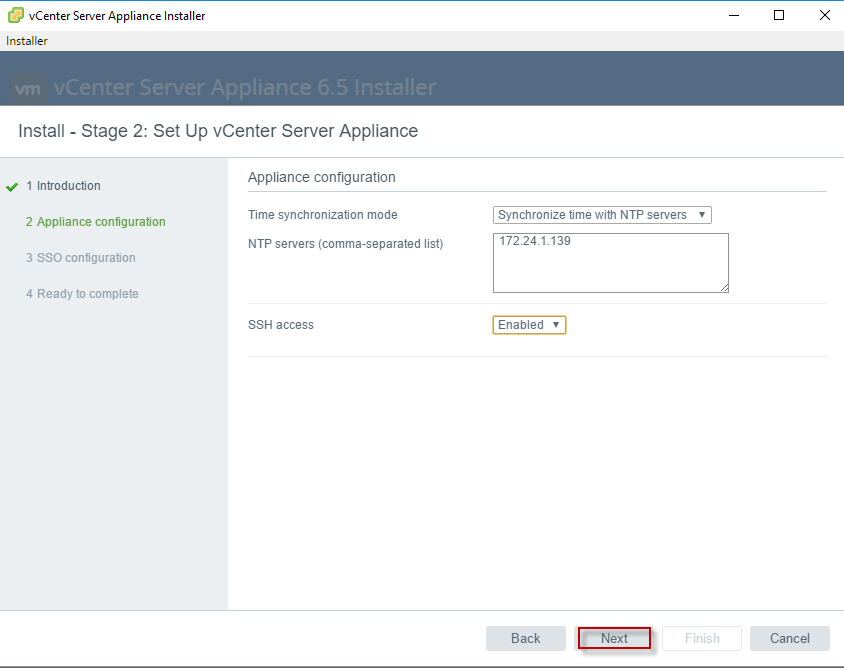


With this now we need to configure the SSO for the vCenter server to complete the deployment.

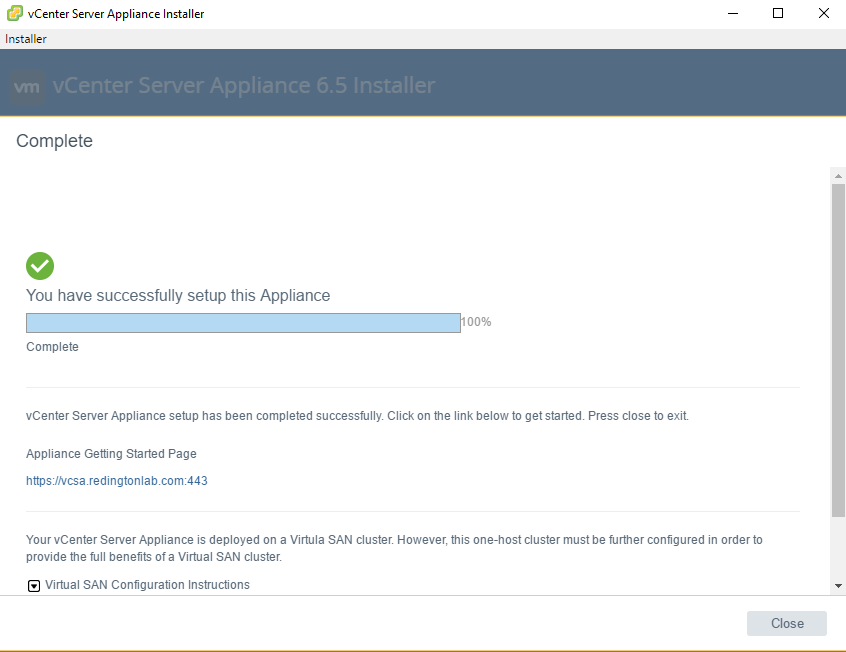
That’s it for this post , I have covered the expansion of vSAN datastore by claiming storage resources from rest of the hosts in below post :






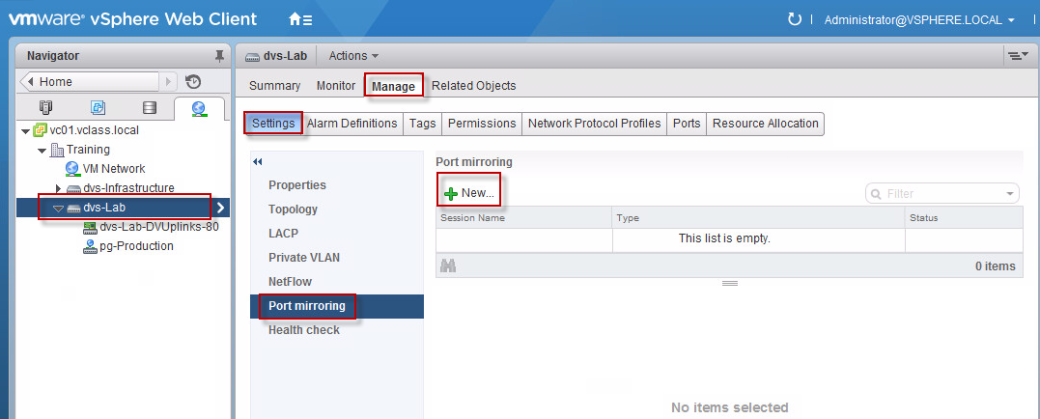







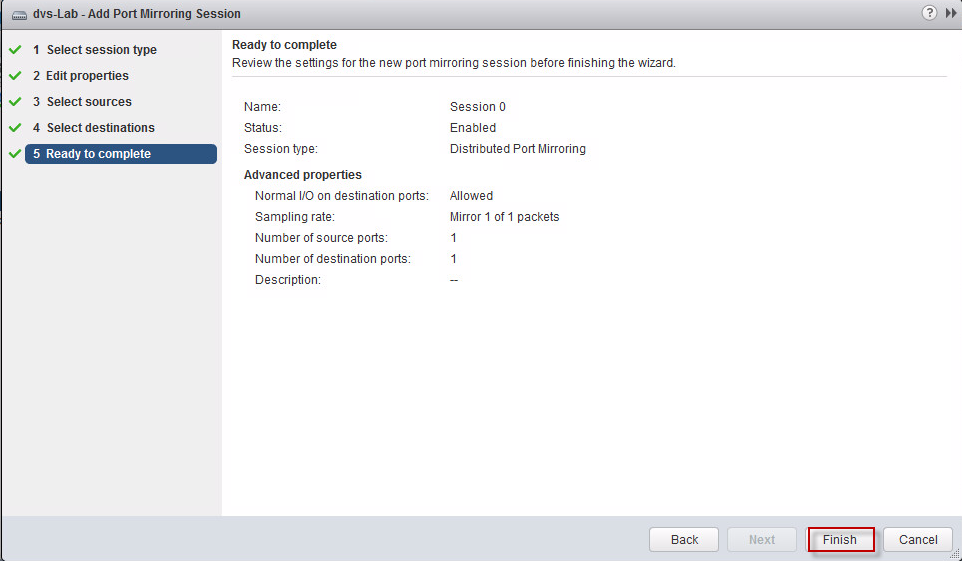





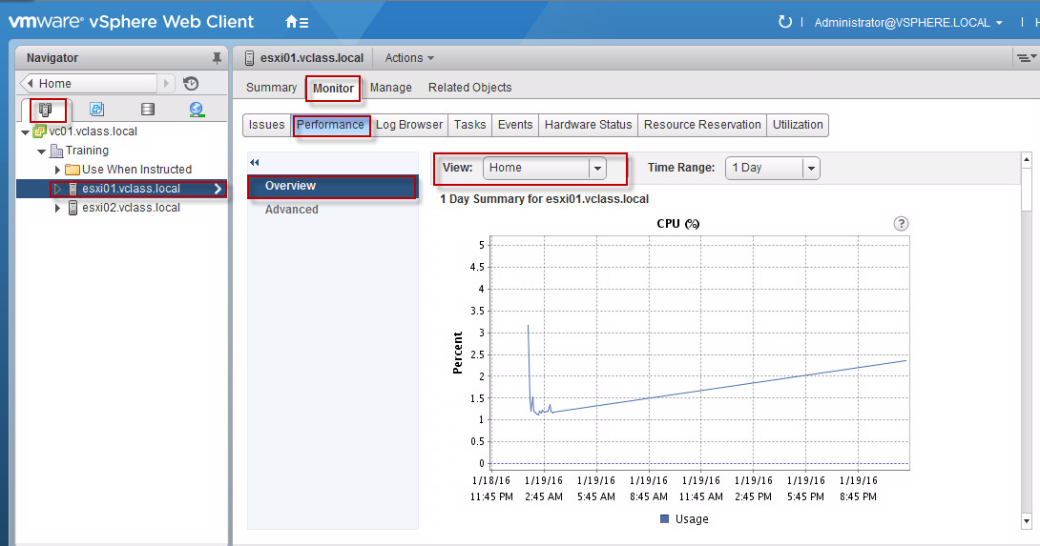
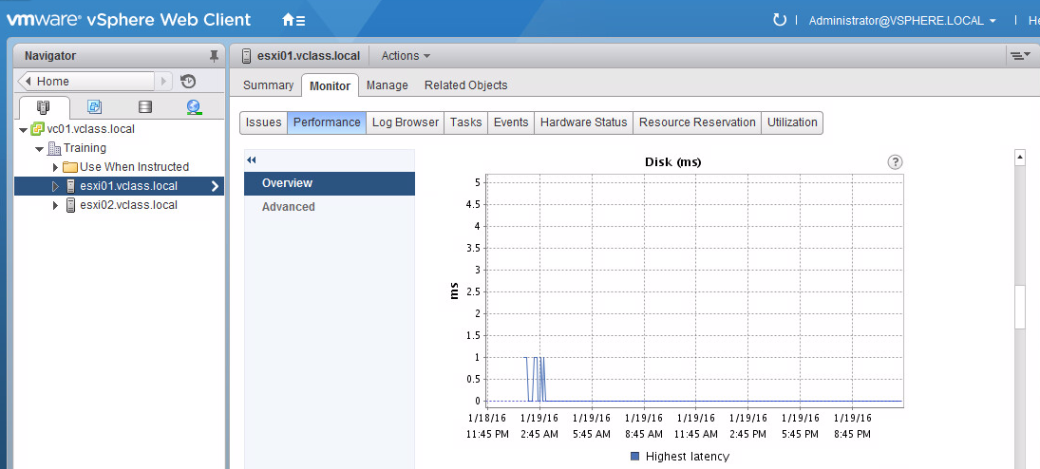
 (vii) In the Chart Metrics panel on the left side of the window, verify that only Memory is selected.
(vii) In the Chart Metrics panel on the left side of the window, verify that only Memory is selected.
 (i) Examine the performance chart legend.
(i) Examine the performance chart legend.

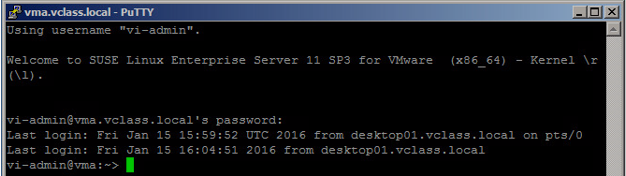





 1.Display the CPU characteristics of the ESXi host.
1.Display the CPU characteristics of the ESXi host.

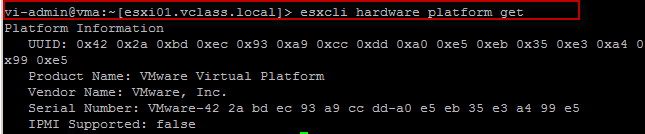
 5.Display the time and date on the host.
5.Display the time and date on the host. 8.Last command i want to highlight is vicfg-ntp commands in the vSphere Management Assistant which you can use to query and configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) settings.
8.Last command i want to highlight is vicfg-ntp commands in the vSphere Management Assistant which you can use to query and configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) settings.





 – At the top of the middle pane, click Actions and select Reboot.
– At the top of the middle pane, click Actions and select Reboot.